A very big branch answer key icivics – Delving into the realm of civics, we embark on an exploration of the legislative branch, often referred to as “a very big branch.” This term holds immense significance in the intricate balance of powers within a government, shaping the dynamics between its various branches.
Throughout history, the legislative branch has undergone a transformative journey, evolving in structure and functions to meet the ever-changing needs of society. Its impact on lawmaking, oversight, and representation is undeniable, and its size and influence continue to be a subject of ongoing debate.
Key Concepts
In the context of civics, “a very big branch” refers to a branch of government that possesses significant power and influence, potentially disrupting the balance of power among the three branches.
The concept of “a very big branch” highlights the importance of maintaining a separation of powers to prevent any one branch from becoming too dominant. This principle ensures that no single entity can exercise excessive authority, thereby safeguarding individual liberties and preventing tyranny.
Impact on Balance of Power
When one branch becomes “very big,” it can disrupt the delicate balance of power among the three branches. This can occur through various mechanisms, such as:
- Legislative Encroachment:The legislature may expand its powers beyond its constitutional authority, infringing upon the executive or judicial branches.
- Executive Overreach:The executive branch may accumulate excessive power, potentially undermining the authority of the legislature or judiciary.
- Judicial Activism:The judiciary may interpret laws in a manner that expands its authority, potentially encroaching upon the other branches.
These scenarios can lead to conflicts between branches, gridlock in government, and a breakdown in the system of checks and balances.
Historical Context
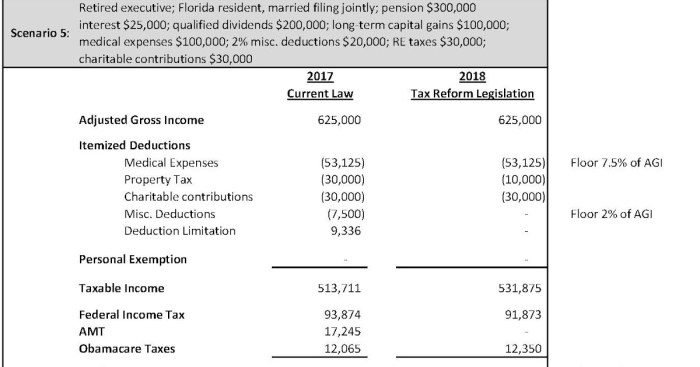
The concept of “a very big branch” in the United States Constitution has its roots in the debates and compromises that shaped the design of the legislative branch. The Framers of the Constitution were acutely aware of the potential for tyranny and sought to create a system of checks and balances to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
The idea of a large legislative branch was first proposed by James Madison in his Federalist Paper No. 51. Madison argued that a large legislature would be more representative of the people and less likely to be swayed by special interests.
He also believed that a large legislature would be more difficult for a single faction to control.
The Framers ultimately decided to create a bicameral legislature, with a Senate and a House of Representatives. The Senate was designed to be a more deliberative body, while the House of Representatives was designed to be more responsive to the will of the people.
This system of checks and balances has helped to ensure that no one branch of government can become too powerful.
The Great Compromise
One of the most important compromises that shaped the design of the legislative branch was the Great Compromise. This compromise resolved the dispute between large and small states over representation in Congress. The Great Compromise created a bicameral legislature, with the Senate representing the states equally and the House of Representatives representing the people in proportion to their population.
The Evolution of “A Very Big Branch”
The concept of “a very big branch” has evolved over time. In the early years of the republic, the legislative branch was the dominant branch of government. However, the rise of the presidency and the Supreme Court in the 20th century has led to a more balanced system of checks and balances.
Today, the legislative branch remains a powerful force in American government. It has the power to make laws, declare war, and impeach the president. However, it is also subject to checks and balances from the other branches of government.
Structure and Functions: A Very Big Branch Answer Key Icivics
The legislative branch of the United States government is a bicameral legislature, consisting of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives is composed of 435 members, each representing a congressional district within a state.
The Senate is composed of 100 members, with each state having two senators.The key functions of the legislative branch include lawmaking, oversight, and representation. Lawmaking is the process of creating new laws or amending existing ones. Oversight is the process of monitoring the actions of the executive branch to ensure that it is operating in accordance with the law.
Representation is the process of representing the interests of constituents in the legislative process.The size of the legislative branch can influence its functions in several ways. First, a larger legislative branch can make it more difficult to pass legislation, as it requires a majority of both the House and the Senate to approve a bill.
Second, a larger legislative branch can make it more difficult to conduct oversight, as it can be more difficult to monitor the actions of the executive branch effectively. Third, a larger legislative branch can make it more difficult to represent the interests of constituents, as each member of Congress represents a larger number of people.
Checks and Balances

The system of checks and balances is a fundamental principle of the United States government. It is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful. The legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch each have their own powers and responsibilities, and they are able to check each other’s power.For
example, the legislative branch can pass laws, but the executive branch can veto those laws. The judicial branch can interpret laws, but the legislative branch can override those interpretations. This system of checks and balances ensures that no one branch of government can become too powerful.
A Very Big Branch
However, a “very big branch” can affect the effectiveness of these checks and balances. A very big branch can have more power than the other branches, and this can make it difficult for the other branches to check its power.For
example, if the legislative branch is much larger than the other branches, it may be able to pass laws that the other branches cannot veto. This can give the legislative branch too much power, and it can make it difficult for the other branches to check its power.
Examples
There are several examples of how a very big branch has influenced the balance of power between the branches.* In the early days of the United States, the legislative branch was much larger than the other branches. This gave the legislative branch a great deal of power, and it was able to pass laws that the other branches could not veto.
This led to a period of time known as the “Era of Good Feelings,” during which the legislative branch was able to pass laws that benefited its own members.
- In the late 19th century, the executive branch became much larger than the other branches. This gave the executive branch a great deal of power, and it was able to take actions that the other branches could not stop.
This led to a period of time known as the “Gilded Age,” during which the executive branch was able to use its power to benefit its own interests.
- In the 20th century, the judicial branch became much larger than the other branches. This gave the judicial branch a great deal of power, and it was able to make decisions that the other branches could not overturn. This led to a period of time known as the “Warren Court Era,” during which the judicial branch was able to use its power to make sweeping changes to American society.
These are just a few examples of how a very big branch can influence the balance of power between the branches. It is important to remember that the system of checks and balances is designed to prevent any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
However, a very big branch can make it difficult for the other branches to check its power.
Contemporary Issues
The legislative branch faces numerous contemporary challenges that impact its structure and functions. These include the influence of technology, globalization, and political polarization.
Impact of Technology
Technology has transformed the legislative process. The internet has made it easier for constituents to contact their representatives and for representatives to share information with their constituents. Social media has also emerged as a powerful tool for political communication. However, technology has also raised concerns about privacy, misinformation, and the potential for foreign interference in elections.
Impact of Globalization
Globalization has increased the interconnectedness of the world economy. This has made it more difficult for governments to regulate economic activity. It has also led to increased competition for jobs and resources. These challenges have put pressure on the legislative branch to find ways to promote economic growth and protect the interests of its citizens.
Impact of Political Polarization, A very big branch answer key icivics
Political polarization has become increasingly common in recent years. This has made it more difficult for the legislative branch to reach consensus on important issues. Partisan gridlock has become a major problem, preventing the passage of legislation and making it difficult for the government to function effectively.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of the term “a very big branch”?
The term “a very big branch” emphasizes the size and influence of the legislative branch in the separation of powers, often attributed to its broad lawmaking authority and its ability to shape policies that impact the nation.
How does the legislative branch influence the balance of power?
Through its legislative functions, oversight responsibilities, and power to impeach, the legislative branch can check the powers of the executive and judicial branches, ensuring a system of checks and balances that prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful.
What are some contemporary issues facing the legislative branch?
The legislative branch faces challenges such as partisan gridlock, the influence of special interest groups, and the impact of technology on political discourse, which can hinder its ability to effectively carry out its functions.