Select the True Statements About Protein Secondary Structure: Embark on a journey into the intricate world of proteins, where structure dictates function. Delve into the fascinating realm of alpha-helices, beta-sheets, and random coils, unraveling the secrets that govern their formation and stability.
Secondary structures are the foundation upon which the complex architecture of proteins is built. They determine the overall shape and function of these vital biological molecules. Join us as we explore the intricate interplay between amino acid sequences, hydrogen bonding, and the factors that influence the formation of these fundamental protein building blocks.
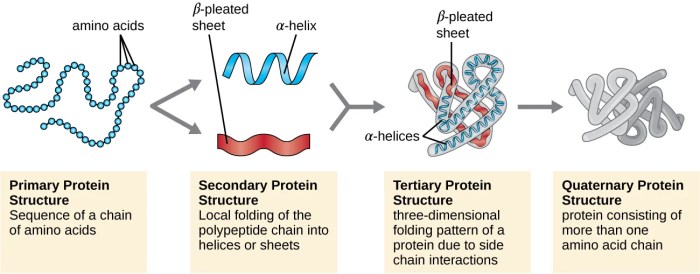
Protein Secondary Structure Overview
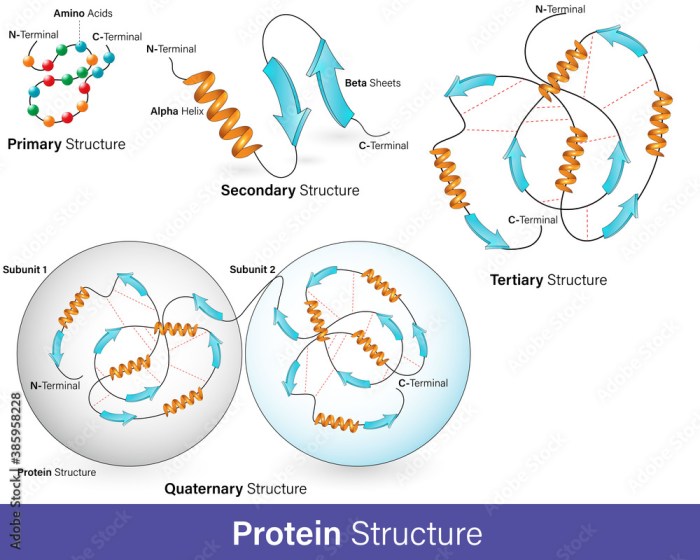
Protein secondary structure refers to the local spatial arrangement of amino acids within a polypeptide chain. It is an intermediate level of protein organization, between the primary structure (the sequence of amino acids) and the tertiary structure (the overall three-dimensional shape of the protein).
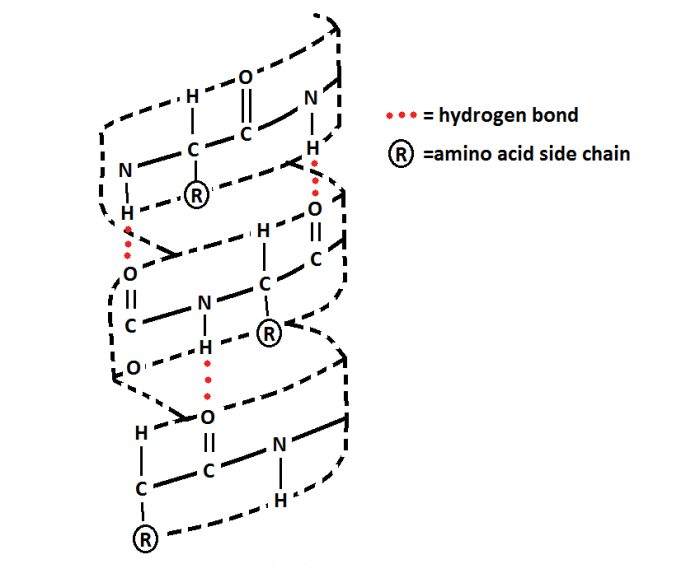
Secondary structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the backbone amide and carbonyl groups of amino acids. The two most common types of secondary structures are the alpha-helix and the beta-sheet.
The formation of secondary structures is influenced by a number of factors, including the amino acid sequence, the presence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids, and the temperature and pH of the environment.
Alpha-Helix Structure
The alpha-helix is a right-handed helical structure in which the amino acid backbone forms a regular coil. The hydrogen bonds in an alpha-helix are formed between the carbonyl oxygen of one amino acid and the amide hydrogen of the amino acid four residues further along the chain.
Alpha-helices are typically found in proteins that are involved in structural roles, such as the cytoskeleton and muscle proteins.
Beta-Sheet Structure
The beta-sheet is a pleated sheet structure in which the amino acid backbone forms a series of parallel or antiparallel strands. The hydrogen bonds in a beta-sheet are formed between the carbonyl oxygen of one amino acid and the amide hydrogen of the amino acid two residues further along the chain.
Beta-sheets are typically found in proteins that are involved in enzymatic reactions, such as antibodies and enzymes.
Random Coil Structure
The random coil is a disordered structure in which the amino acid backbone does not form any regular pattern. Random coils are typically found in proteins that are unfolded or in the process of folding.
Relationship between Secondary and Tertiary Structure
Secondary structures interact with each other to form the tertiary structure of a protein. The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein, and it is determined by the interactions between the secondary structures.
The tertiary structure of a protein is important for its function. The shape of a protein determines its ability to bind to other molecules and to carry out its biological role.
Methods for Determining Secondary Structure, Select the true statements about protein secondary structure
There are a number of experimental techniques that can be used to determine the secondary structure of a protein. These techniques include X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and circular dichroism spectroscopy.
X-ray crystallography is the most accurate method for determining the secondary structure of a protein. However, it is also the most expensive and time-consuming method.
NMR spectroscopy is a less accurate method than X-ray crystallography, but it is also less expensive and time-consuming. NMR spectroscopy can be used to determine the secondary structure of proteins in solution.
Circular dichroism spectroscopy is a relatively inexpensive and time-consuming method for determining the secondary structure of proteins. However, it is less accurate than X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy.
User Queries: Select The True Statements About Protein Secondary Structure
What is the significance of protein secondary structure?
Protein secondary structure plays a crucial role in determining the overall shape and function of proteins. It provides stability, facilitates interactions with other molecules, and influences protein dynamics.
How are alpha-helices and beta-sheets stabilized?
Alpha-helices are stabilized by intramolecular hydrogen bonding between the backbone NH and CO groups of amino acids. Beta-sheets are stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonding between the backbone NH and CO groups of adjacent strands.
What factors influence the formation of random coils?
The formation of random coils is influenced by the amino acid sequence, temperature, pH, and the presence of denaturants. Regions with high proportions of hydrophilic amino acids tend to form random coils.