Embark on an academic journey with our comprehensive Long Run Aggregate Supply Activity 3-8 Answer Key. Delve into the intricacies of LRAS, unraveling its profound implications for economic growth and policymaking. Our meticulously crafted guide empowers you with a deep understanding of this fundamental economic concept, equipping you to navigate the complexities of modern economic landscapes.
Within these pages, you will discover the essence of LRAS, exploring its determinants and the factors that shape its shifts. Witness the interplay between LRAS and economic growth, deciphering its pivotal role in determining potential GDP and long-term economic prosperity.
Moreover, we illuminate the policy implications of LRAS, empowering you to analyze the effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policies and navigate the delicate balance in managing this crucial economic indicator.
Overview of Long-Run Aggregate Supply: Long Run Aggregate Supply Activity 3-8 Answer Key
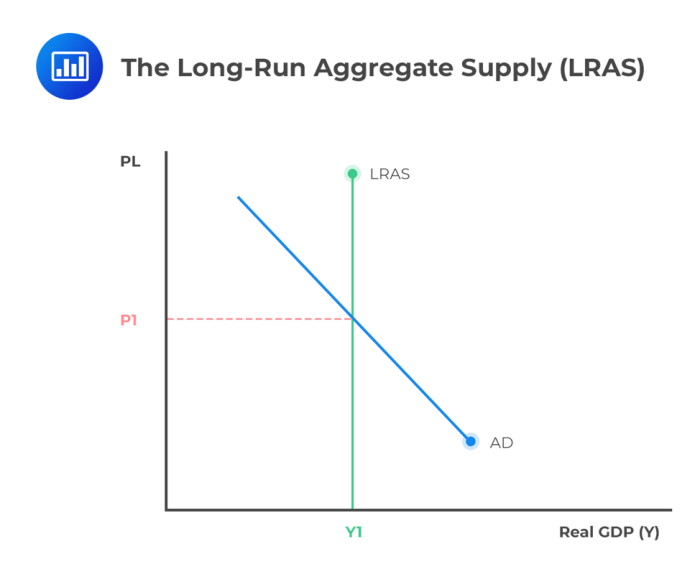
Long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) represents the total output an economy can produce at a given price level when all factors of production are fully utilized and operating efficiently. It is also referred to as potential output, which is the maximum sustainable level of output an economy can achieve without experiencing inflationary pressures.
LRAS is determined by several factors, including:
- Labor force size and quality
- Capital stock
- Technological progress
- Institutional factors (e.g., property rights, legal system)
Determinants of Long-Run Aggregate Supply
Labor Force Size and Quality
The size and quality of the labor force play a crucial role in determining LRAS. A larger and more skilled labor force can produce more output, leading to a higher LRAS.
Capital Stock
Capital stock refers to the physical assets used in production, such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure. A larger and more advanced capital stock enables workers to be more productive, resulting in a higher LRAS.
Technological Progress
Technological progress leads to new and more efficient ways of producing goods and services. This increases productivity and allows for higher output levels, shifting LRAS to the right.
Institutional Factors
Institutional factors, such as property rights and the legal system, can also affect LRAS. Secure property rights encourage investment and innovation, while a well-functioning legal system facilitates efficient production and distribution of goods and services.
Shifts in Long-Run Aggregate Supply, Long run aggregate supply activity 3-8 answer key
LRAS can shift due to changes in any of the determinants discussed above. For example:
- An increase in the labor force or an improvement in labor skills can shift LRAS to the right.
- An increase in capital stock or technological progress can also shift LRAS to the right.
- Conversely, a decrease in any of these factors can shift LRAS to the left.
Shifts in LRAS have significant implications for the economy. A rightward shift leads to an increase in potential output, while a leftward shift results in a decrease in potential output.
Long-Run Aggregate Supply and Economic Growth
LRAS plays a central role in determining an economy’s long-term growth potential. A higher LRAS implies a higher potential GDP, indicating the economy’s capacity to produce goods and services.
Factors that promote long-term economic growth, such as investment in education, infrastructure, and technology, contribute to a rightward shift in LRAS.
Policy Implications of Long-Run Aggregate Supply
LRAS affects the effectiveness of monetary and fiscal policy. Monetary policy, which involves managing interest rates, has a limited impact on LRAS in the long run.
Fiscal policy, on the other hand, can influence LRAS by affecting factors such as labor supply, capital accumulation, and technological progress. However, it is important to consider the trade-offs involved in managing LRAS, as policies aimed at shifting LRAS to the right may have short-term costs.
General Inquiries
What is the significance of Long Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)?
LRAS serves as a crucial determinant of an economy’s potential output and long-term economic growth.
How do shifts in LRAS impact the economy?
Shifts in LRAS can significantly influence inflation, unemployment, and overall economic activity.
What factors can promote or hinder long-term economic growth?
Factors such as technological progress, labor force quality, and institutional stability play vital roles in fostering or impeding long-term economic growth.